
About Diabetes
What is Diabetes?
In our normal day to day lives, we need food for energy and maintenance of our health. Any form of food that contains carbohydrates (starchy food, sugary food, milk & dairy products, fruit) is broken down into glucose in the stomach.
This glucose then travels through the blood stream, which causes the blood glucose levels of the body to rise. The body then instructs a gland called the pancreas to produce insulin. Insulin is a hormone helps the body get the energy it needs from food. Insulin acts like sort of a key to the doors of the cells, it is used for the better absorption and distribution of glucose throughout the body. Glucose is then absorbed by the cells of the body & the blood glucose level goes down. This Process of Insulin production and maintenance of optimum blood glucose level is essential for our body to remain healthy.

Diabetes is an Auto immune / Lifestyle disorder that causes the blood sugar level of the body to rise, due to the inadequate or non-production of the Insulin by the pancreas.
There are 2 Main Types of Diabetes :
Type-1
In Type-1 Diabetes, the pancreas does not make insulin. The immune system attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that make insulin. Type-1 Diabetes is usually diagnosed in childhood and adolescence, although it can appear at any age. People with Type-1 Diabetes need to take insulin every day. 10% of the total people suffering from diabetes have Type-1 Diabetes.
Type-2
In Type-2 Diabetes, the body doesn’t utilize or make enough insulin for the absorption of glucose. Onset of Type-2 Diabetes happens at any age, even during childhood. However, this type of diabetes occurs most often in middle-aged and older people. Type-2 is the most common type of diabetes. 90% of the total people suffering from diabetes have Type-2 Diabetes.
It is more likely to develop Type-2 Diabetes, if :
- Age is 45 or older
- Has Insulin Resistance
- Suffered Damage or removal of the pancreas.
- Have a family history of diabetes.
- Overweight & Physical inactivity.
- High blood pressure.
Research by the World Health Organization (WHO) on diabetes
- The number of people with diabetes has risen from 108 million in 1980 to 422 million in 2014.
- The global prevalence of diabetes among adults over 18 years of age has risen from 4.7% in 1980 to 8.5% in 2014 (1).
- Diabetes prevalence has been rising more rapidly in middle- and low-income countries.
- Diabetes is a major cause of blindness, kidney failure, heart attacks, stroke and lower limb amputation.
- In 2015, an estimated 1.6 million deaths were directly caused by diabetes. Another 2.2 million deaths were attributable to high blood glucose in 2012.
Almost half of all deaths attributable to high blood glucose occur before the age of 70 years. - WHO projects that diabetes will be the seventh leading cause of death in 2030(1).

Symptoms & Other Disease onsets
Symptoms of diabetes include the following
- Increased hunger
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Numbness or tingling in the feet or hands
- Sores that do not heal
- unexplained weight loss
Over time, high blood glucose leads to comorbidities such as
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Kidney disease
- Eye problems
- Dental disease
- Foot problems
Treatment
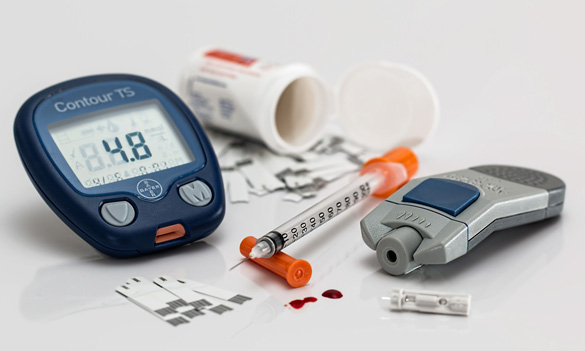
There is no cure for diabetes, but there are various treatments that can effectively reduce the symptoms and help in the management of the disorder.
For Type-1 Diabetes: Insulin syringes and pumps are mandatory for the continual supply of insulin at regular intervals.
For Type-2 Diabetes: Oral medication and insulin, as prescribed by a diabetologist after examination of patient history. Change in diet, increase in physical activity and weight loss also are effective ways of managing diabetes.
Prevention
As we mentioned earlier, Diabetes is a lifestyle disorder, it’s onset can be prevented and managed by following the below points. These lifestyle changes will not only help prevent diabetes but also will also push you towards a healthy Life.
- Cut Sugar and Refined Carbs from Your Diet.
- Exercise Regularly.
- Continuously drink water at regular intervals.
- Lose Weight if Overweight/Obese.
- Quit Smoking.
- Eat Loads of Fibre Based Foods.
- Get a Health check-up done quarterly.

